The LTO Tracker is an online platform jointly developed by the Land Transportation Office (LTO) and the Department of Transportation (DOTr) that allows motorists in the Philippines to check the availability and delivery status of their driver’s license and vehicle plate number in real-time without the hassle of repeated LTO trips.
If you’ve been waiting for your driver’s license or vehicle plate number and don’t want to keep making trips to the LTO just to check, the LTO Tracker now offers a convenient, transparent, and secure way to monitor the status of your license or plate from your phone or computer — and even have it delivered right to your doorstep, allowing you to save time and avoid the stress of long queues.
What Does it Do?
The LTO Tracker is a convenient, transparent, and secure online platform that allows motorists in the Philippines to check the availability and delivery status of their driver’s license and vehicle plate number online in real-time. Through this online LTO tracker, users can:
- Search for license and plate availability
- Request home delivery via LTO-accredited couriers
- Track delivery progress online
Note that despite the availability of options to deliver the license via the LTO tracker, foreign driver’s license conversions are still not eligible for delivery and must be sent through the Philippine Postal Service as per the LTO memorandum dated December 23, 2019.
What Is it For?
The online LTO tracker was created for:
- Convenience: Check status anytime, anywhere.
- Faster service: Reduce unnecessary trips and waiting time at LTO offices.
- Transparency: View real-time updates on application and delivery status.
- Accessibility: Provide an online alternative to in-person follow-ups.
Benefits of Using LTO Tracker
With the No Plate, No Travel policy, having quick access to plate status is a big help. The tracker:
- Saves time by avoiding unnecessary LTO visits
- Helps avoid fines by knowing exactly when your plate is ready
- Lets you opt for home delivery, similar to passport or PSA document drop-offs
- Lets you monitor your license or plate’s progress online.
- Allows you to have it shipped securely to your home.
- Helps protect your personal information using advanced security systems.
Who Can Use
The LTO Tracker was created with the following users in mind:
- Motorists in the Philippines waiting for their driver’s license or vehicle plate number
- Vehicle owners who recently bought a new car or motorcycle and are waiting for their plates
- Motorists who renewed their driver’s license and need to check its availability
- Owners requesting replacement plates or licenses due to loss, damage, or change of details
- People who prefer home delivery of their license or plate instead of in-person pick-up
- Those with internet access who want to track updates online
Note: This is not for foreign driver’s license conversions — these are delivered only via the Philippine Postal Service as per LTO policy
Requirements
Here’s what you need to prepare to use the LTO Tracker without any hassle:
- For Driver’s License tracking:
- Driver’s license number
- Birthdate
- LTMS client number (if your record isn’t found)
- For License Plate tracking:
- Plate number or 15-digit MV (Motor Vehicle) file number from your Certificate of Registration (CR)
- Additional details if not found in the system: name, birthdate, OR/CR details, email, phone number, and LTO transaction location
- For Delivery Requests:
- Clear photo of a valid government-issued ID
- Copy of OR (Official Receipt) and CR (Certificate of Registration) for the vehicle
- Complete delivery address
- Payment for courier fee via GCash or QRPh
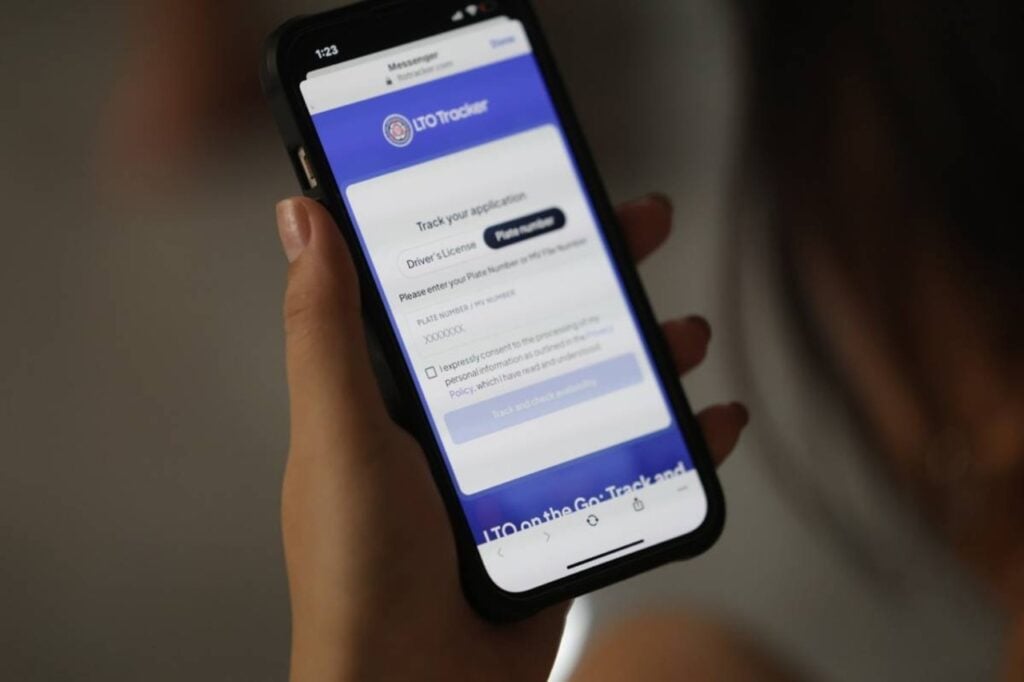
How to Use the LTO Tracker
To use the tracker, simply follow these steps:
Step 1. Go to the official website
Visit https://ltotracker.com. Only use the official site.
Step 2. Choose the service
Select either Driver’s License or License Plate.
Step 3. Enter your details
- For license: Input your license number and birthdate.
- For plates: Enter your plate number or the 15-digit MV file number from your Certificate of Registration (CR).
Step 4. Check the status
Results may show: In Process, Dispatched, Ready for Pick-Up, or Available for Delivery.
Step 5. Select pick-up or delivery
- For delivery: Upload a photo of your valid ID and OR/CR, provide your address.
- Pay the delivery fee via GCash or QRPh. Rates vary by location.
Step 6. Track delivery progress
Once booked, you can follow the status until it arrives.
Fees
Here are the fees associated with using LTO Tracker:
- Delivery fee varies by location — If you opt for home delivery of your driver’s license or plate number, you’ll pay a courier fee that changes depending on where you are in the Philippines.
- Payment via e-wallet — You can settle this delivery fee using GCash or QRPh.
- Examples from user experience:
- One user reported a delivery fee of ₱158.49 for plate delivery within Quezon City.
- Another user located outside Metro Manila shared having paid ₱240 for shipping their license to Cebu City.
- A separate user mentioned paying ₱159 for delivery via GogoExpress.
Reminders
When using LTO Tracker, make sure that you are ready to:
- Provide accurate and complete personal details
- Name
- Address
- Contact details
- Use the platform only for lawful purposes
- Avoid fraudulent or harmful activities
- Follow applicable Philippine laws and regulations
You may also want to take note of the following:
- The LTO Tracker acts as an intermediary between users and delivery service providers.
- Delivery time and condition are handled by the courier.
- Any delivery disputes must be taken up directly with the courier company.
- LTO does not guarantee complete accuracy of online data at all times.
- LTO is not liable for content errors, delays, or damages arising from site use.
- Service access can be terminated without notice for any reason.
- Terms of Use may change periodically; users should check for updates.
Video: How to Use the LTO Tracker
For a visual walkthrough on how to use the LTO Tracker, you may watch this video below:
Contact Information
For inquiries and other concerns, you may reach out to LTO via the following:
- Email: c3.ltocentral@gmail.com / digital.hub.lto@gmail.com
- Official Contact: ltomailbox@lto.gov.ph

